Functional Organization | Nature of functional foremanship
The limited scope of working to which the line organization is liable, has given raise to another type of organization called “Functional Organization” otherwise known as “Functional Foremanship“. This system was organized by F.W. Tailor, the father of Scientific Management.
Having realized the fact that it is practically impossible for one leader, however skillful, experienced and qualified he may be, to successfully cope with all the functions of an enterprise. Taylor proposed this functional system of organization which gives place for specialization in the organizational structure. As Taylor puts it, the functional system was evolved on the following basis.
- To make use of the principle of specialization.
- To bring out organizational balance.
Table of Contents
Nature of Functional Organization:
The functional system, as the name suggests divides the whole work into various functions. Each function is entrusted to a functional foreman who is generally a specialist in that particular function. The worker should receive instructions from all of them. Each functional foreman is placed at the same authoritative level.
Taylor’s plan of Functional Foremanship is illustrated below:
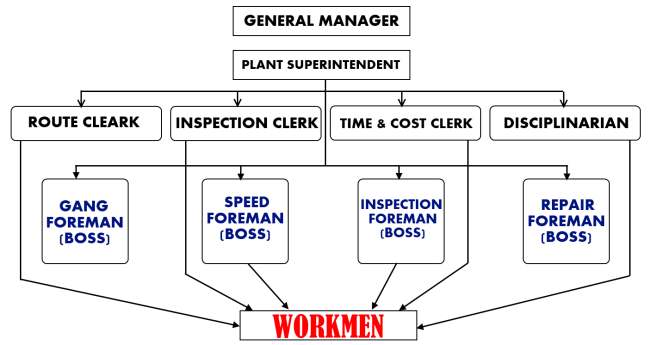
Taylor divided the supervisory functions into two divisions viz.,
- Office or Planning division, and
- Factory Division.
The functions of the two divisions are performed by eight foremen.
Foremen in the Office Division:
The office or planning department consists of the following foremen.
1. The Route Clerk: The route clerk is responsible for ascertaining the actual route through which whole work process travel from conversion of raw materials into finished products.
2. Instruction Card Clerk: He prescribes the exact method of completing a work according to the route specified.
3. Time and Cost Clerk: He specified the standard time for the completion of the work and also fixes the time schedule for each element of the job. He also looks after the work relating to payroll and cost. Recent tendency is to split up the functions of this clerk into two separate units – the pay roll department and the cost department.
4. Shop Disciplinarian: He acts as a personnel manger and deals with the cases of indiscipline and absenteeism. Thus, his primary function is to maintain orderliness in the factory and office.
Foremen in the factory Division:
The factory division consists of the following four foremen:
1. Gang Boss: The gang boss is concerned with the preparation of work for the machine such as the set up of machine, moving work from machine to machine and from machine to stores.
2. Speed Boss: He is in charge of technical supervision of the work. Such as correcting the speed of the work, flow of work from one place to another, etc. Now-a-days he is designated as Assistant Foreman.
3. Inspector: The inspector is entrusted with all inspection and testing works. He is responsible for the quality of the product.
4. Repair Boss: The repair boss is entrusted with the task of proper repair and maintenance of the equipment and up-keep of the plant.
While developing the concept, Taylor suggested that it is unscientific to over load a foreman with entire responsibility of running a department. He advocated that the direction of work should be decided by functions and not by authority. Hence, his main emphasis was on functions.
Functional organization can also operate at higher level management. The whole work of the organization should be divided into various departments viz., purchase, sales, finance, production, etc; The respective managers will be responsible for carrying out the various activities of their departments in the organization.

