Factors determining buyer behavior
Table of Contents
Factors determining buyer behavior
There are various factors that determine buyer behaviour such as Geographic factors, Demographic factors, Cultural factors, Social factors and Socioeconomic factors as seen in the following diagram.
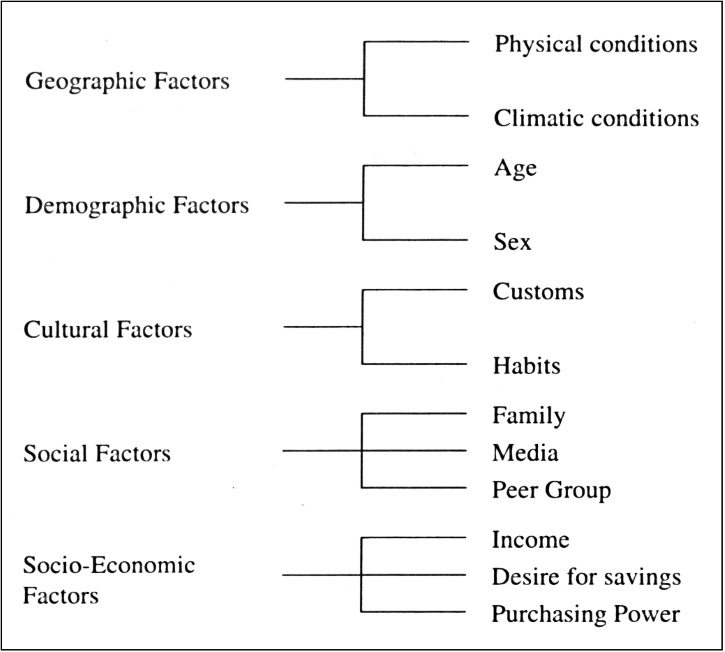
1. Geographic Factors that determine buyer behavior
Physical Conditions
Every place has its own physical conditions which determine the buying behavior of the consumers.
For example, bullock carts are used as a mode of transport by the people in villages due to lack of proper roads. In cities, such carts are used mainly for transporting goods.
Thus, a person, aspiring to be a two-wheeler or four-wheeler dealer, would like to have his show room in a city rather than in a village.
Climatic Conditions
People living in hill stations always experience a cold climate. Such a climatic condition forces them to use sweaters, waistcoats, caps, etc. These goods are not so popular with the city dwellers who always experience a hot climate. A person marketing air-conditioners cannot have his showroom in a hill station.
2. Demographic factors that determine buyer behavior
Age
The age of the consumers determines their buying behavior. Children desire to have toys, chocolates, etc. Those in their adulthood need certain products like shaving cream, cosmetic items, etc.
Generally, people who are in their old-age need certain items like spectacles, walking stick, medicines, etc. In our markets, there are shops that exclusively cater to children. It may be remembered that the Indian Railways offer tickets at concessional rates- and also provide special quota to the senior citizens.
Sex
Certain products are desired by men and certain others by women. Leather belts, shoes, shaving kit etc., are the products used by men. Bangles, studs, lipstick etc., are the products used by women. In Indian markets, there are certain shops that cater only to men and certain others that cater only to women.
3. Cultural factors that determine buyer behavior
Customs
The buying behavior of the people will be very much influenced by their customs and practices.
For example, people in the North eat chapattis whereas in the South rice is the major food item. Again, in the South men prefer Dhoties whereas men in the North prefer Pyjamas. A cloth merchant in Chennai, therefore, may not stack large quantities of pyjamas.
Habits
Customs and practices are inherited. Habits are acquired and not inherited.
For example, Noodles and Pizzas are not our type of food. But we have acquired a taste for such items. As a result, these are being sold in every nook and corner of our cities and towns.
4. Social factors that determine buyer behavior
Family Influence
A person’s buying behavior is very much influenced by his family. The father or the mother may decide what they should buy for their children. Likewise, if there are two sisters, probably the elder sister will suggest to her younger sister what is good for her.
Media Influence
The influence of media, cinema in particular, on a person’s buying behavior cannot be ignored. Most of the youngsters emulate their favorite film heroes in hairstyles, dress and so on.
Peer Group Influence
Peer group consists of members who all posses identical characteristics. They all have similar tastes, preferences and so on. Needless to say, every member of such a group will faithfully accept the suggestions of the other members.
5. Socioeconomic factors
Income
Needless to say, an increase in a person’s income may motivate him to go in for new items. He may buy something for himself or for his wife or children.
Desire for Savings
Sometimes, when there is an increase in an individual’s income, he may desire to save a portion of it. The amount so saved may be invested. He may invest in gold, shares, land and so on.
Purchasing Power
The purchasing power of an individual is determined by his real income. There is a difference between money income and real income. Money income refers to the actual amount received as income by a person.
On the other hand, real income refers to the capacity of a person’s money income to buy goods and services. An increase in money income need not result in an increase in real income /purchasing power.

